Self-efficacy plays a crucial role in the world of health and self-development. Self-efficacy has been shown to have a positive impact on our mental well-being, our general health behavior and our physical reactions to events in everyday life. When coping with difficult situations and critical life events in particular, it is important to maintain confidence in your own effectiveness, even when being confronted with new tasks, situations or roles.
But how is self-efficacy actually characterized? How can it be encouraged and practiced? And what role does self-management play in this context? If you want to find out more about how you can use your own power for better health and a fulfilling life, you've come to the right place.
What is self-efficacy?
Self-efficacy describes a person's conviction that they can bring about the desired results based on their own competencies. The concept of self-efficacy was popularized by the renowned Canadian psychologist Albert Bandura in the 1970s. He emphasized that self-efficacy has a strong influence on a person's behavior, mindset and emotional resilience.
The specialist journal of Psychology for Health Sciences explains the concept as follows:
"Self-efficacy is the belief that one can achieve goals through one's own abilities and resources and successfully overcome obstacles along the way (Bandura, 1997; Lazarus & Folkman, 1986; Schwarzer, 2000). A person's belief in their own effectiveness influences their perception, motivation and performance. A high expectation of self-efficacy has positive effects on one's own effort, perseverance and stamina as well as on active coping behavior (Schwarzer, 2000). Self-efficacy and self-esteem are characteristics that are closely linked."
Examples: high vs. low self-efficacy
Self-efficacious people believe in their success and focus on what they can influence themselves. They seize opportunities and set themselves realistic, challenging goals. And they persevere, even in the face of setbacks.
People with low self-efficacy expectations are more likely to assume failure. They see limits rather than opportunities and avoid difficult tasks. They also give up quickly when faced with challenges.

Self-management: the practical implementation of self-efficacy
While self-efficacy describes the confidence you have in yourself, self-management refers to the ability to use your own resources effectively in order to successfully complete certain tasks. Self-management is, so to speak, the practical implementation of self-efficacy beliefs. It means taking responsibility for your actions, regardless of external circumstances. Self-management involves planning, organizing and prioritizing tasks as well as the ability to motivate and discipline yourself to achieve the goals you have set for yourself.
In the health context, self-management is defined by the World Health Organization (WHO) as follows:
"The ability of individuals, families and communities to promote health, prevent illness and maintain health... to cope with illness and disability with or without the support of a healthcare provider".
In other words: "I am responsible for my health and have the means to manage it."
How to increase your self-efficacy
Self-efficacy can be learned and trained - it can be exercised like a muscle. The following strategies can help you to increase your self-efficacy and promote good self-management.
- Self-observation and organization
Self-observation is about understanding your habits, behaviors and emotional reactions. Self-observation techniques such as journaling can help you to recognize your patterns and identify your own needs. Observe yourself carefully to react to changes and organize your tasks and time effectively to achieve your goals. You can also create calendar entries or digital reminders. - Focus on what you can change
Being able to recognize the difference between the things you can change and the things you cannot influence will help you to strengthen your resilience. All too often we waste thoughts and energy on things that affect us but over which we have no control. This energy is better invested in the things we can actually influence.
With his "Circles of Influence" concept, the American self-help author Stephen Covey offers a tool for recognizing the things that are within your control and separating them from things that are beyond your control.
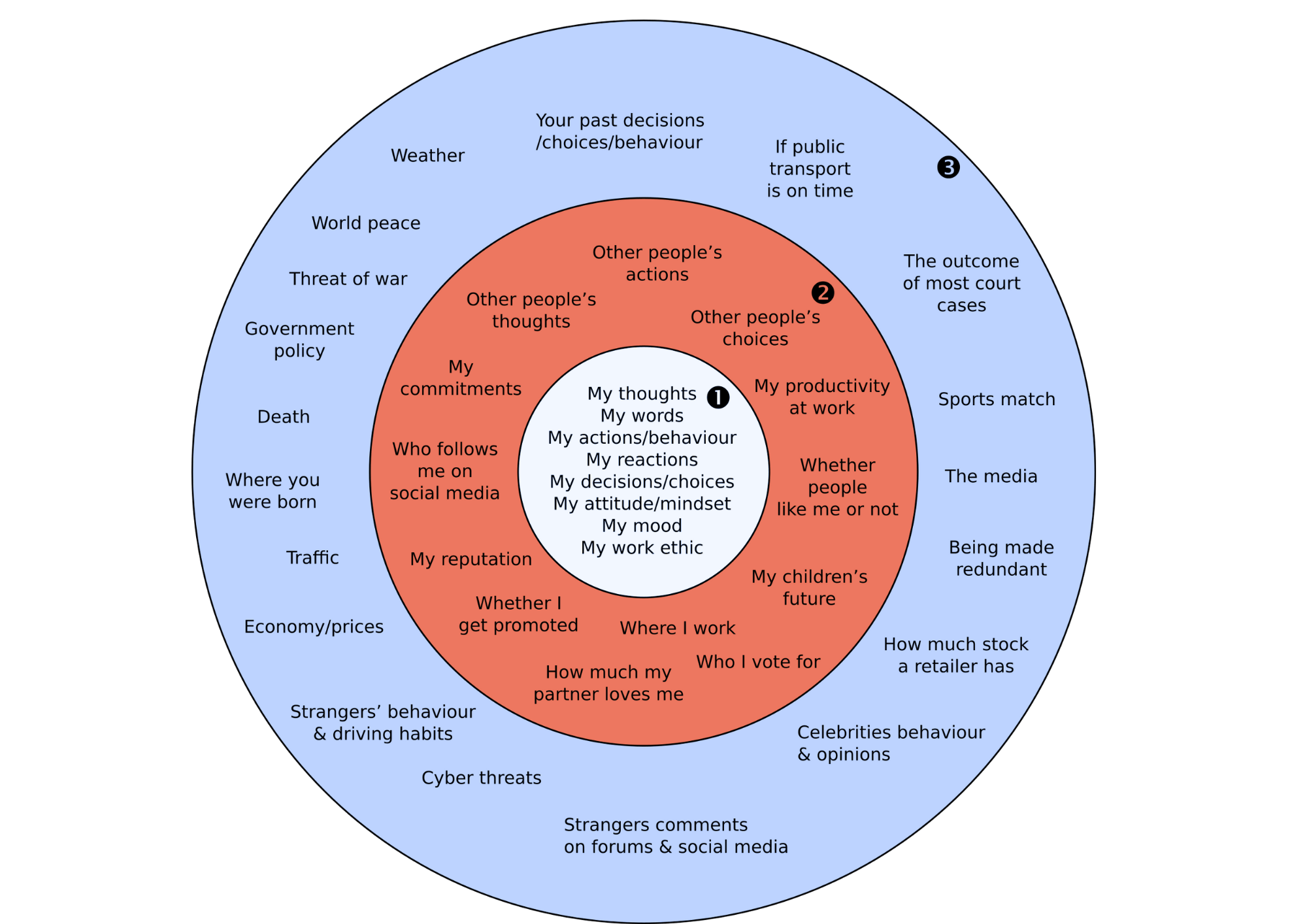
As can be seen in the picture above, we have no influence over a large part of our concerns (3). Consciously separating these concerns from things that can be influenced (2) or controlled (1) creates the capacity to take care of the relevant issues.
- Set SMART goals
Use the SMART rule to set yourself a well-formulated, concise goal. SMART not only means clever in this context, it also describes how a clever goal is put together. SMART stands for the following characteristics:
- Specific (the goal must be precisely formulated)
- Measurable (the achievement or non-achievement must be measurable)
- Appealing (the goal should be attractive, it should motivate you)
- Realistic (it should be feasible)
- Time-bound (a deadline must be set for achieving the goal)
So, an example of a not so smart goal would be: "I want to run a marathon."
An example of a SMART goal is: "I want to run the [LOCATION] marathon on [DATE] and finish in under [TIME] hours. To achieve this, I will train at least [FREQUENCY] per week from [MONTH] to [MONTH]."
The marathon is an example of a very big sporting goal. The SMART rule can easily be applied to all areas of life, be it health, wellness, work, leisure or relationships.
- Self-recognition
Write down your successes in a success diary. You can answer the following questions there: What did I do particularly well today? What have I learned today? What difficult situations have I mastered well? And: praise yourself and give yourself recognition when you have achieved your goals, no matter how small the steps. - Use external resources
Self-efficacy does not mean that you have to master everything in life on your own. On the contrary: part of self-efficacy is recognizing where your limits lie and in which areas you need support from other people. Make effective use of support services such as social networks or professional services.
Akina as a companion on your road to recovery
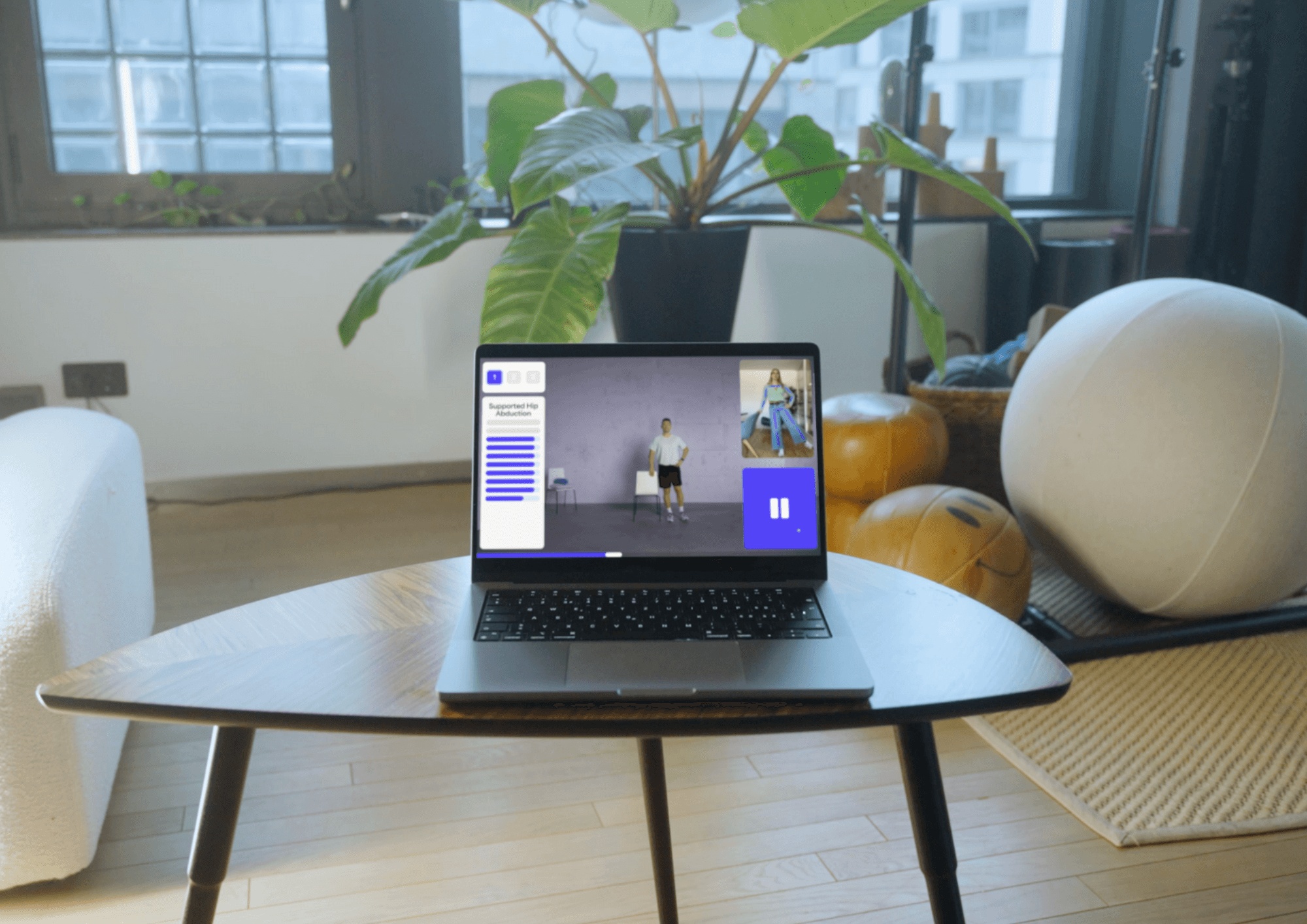
Physiotherapy training at home plays a crucial role in rehabilitation after an injury, operation or illness. If you want to take your health into your own hands, our AI-supported training software is just the thing for you.
Akina Cloud guides you through therapeutic training at home via an interactive, audiovisual platform. Instant AI feedback lets you know whether you are performing the exercise correctly and what you need to pay particular attention to during training. Physiotherapists have the opportunity to evaluate your progress or deficits and adapt your training plan accordingly. This allows patients and therapists to stay in contact and make physiotherapy - and therefore the path to recovery - more efficient.
But that's not all: active movement therapy is also rounded off with informative content and mindfulness meditations to promote a holistic and effective recovery. Click on the button below to try out Akina for yourself soon. We look forward to having you on board!