When it comes to our health, we often think of a balanced diet, plenty of exercise and enough sleep. While these three factors naturally play a big role in our well-being, there is one important detail that often gets far too little attention: a good posture. The posture in which we move is with us continuously throughout our lives: when standing, sitting and even lying down.
Poor posture is very common and can lead to various health problems such as back and neck pain, tension, headaches, breathing or digestive problems. Good posture is not only important for the prevention of pain and injuries, but it can also have an impact on our psyche. In fact, it can help us feel more confident and positive, and be perceived as such by others.
Posture - the basics
In general, posture refers to the relative alignment of the body parts to each other. It describes the position created by the interaction of muscles, ligaments and bones - in other words, the posture we position our body in against gravity. It depends on many factors, such as the condition of our skeletal system, our muscle strength, and the health of our ligaments and fascia.
In this context, good posture refers to the condition in which the bones, joints, cartilage, ligaments and muscles are protected from overload, deformation and injury. Also, the organ system can only function optimally when all the supporting structures of the body are in balance.
What are the most common causes of poor posture?
Prolonged sitting in the office everyday life
The BAG (Swiss Federal Office of Public Health) reports that we sit for up to 15 hours a day. The consequences are not only bad posture - long sitting is a risk factor for various diseases, such as diabetes, heart disease, cancer and mental illness. Sitting at a desk for long periods of time is also very stressful for the entire back, including the neck, as we often stare at monitors in the same sitting position for long periods of time. The shoulders hang forward or are tensely pulled up, the head is lowered and the upper back is unnaturally arched. This can result in a one-sided strain. As a result, the back muscles harden or shorten, and a permanent bad posture creeps in.

Spending a lot of time on the cell phone
The so-called "cell phone neck" has developed into a real widespread disease - especially the younger generation is strongly affected by it. Cell phone neck is caused by overloading the cervical spine, as the head is constantly tilted when using a smartphone. The consequences are tension and pain - and even a change in the head bone. One study reports a growth of "horns" up to three centimeters in size on the lower skull - the suspected cause of which is head posture during cell phone use.
Heavy physical work
It is not only long periods of sitting in office jobs that are immensely detrimental to health; hard work in manual occupations also leaves physical traces. The Swiss Accident Insurance Fund (Suva) reports that around 30% of the working population moves heavy loads every day - many suffer musculoskeletal disorders. In particular, frequent lifting and carrying of heavy objects as well as incorrect bending, twisted standing or kneeling over a longer period of time damage the musculoskeletal system. Common long-term consequences are degenerative joint diseases and pain in the back, shoulders, hips or knees.
Severe overweight
In cases of severe obesity, excess fat is often stored on the abdomen. This shifts the body's center of gravity forward, which can lead to a hollow back. In addition, excess fat on the abdomen is often accompanied by weak and tight abdominal muscles - this makes it difficult to maintain balanced body tension, which means that the lumbar region is not adequately supported. The consequences of excess weight are back pain, a restriction in the mobility of the back, an overload or incorrect load on the spine and the promotion of a spinal deformity.
One-sided load
If there is an imbalance between two opposing muscle groups, poor posture can be a result. Unbalanced training of one side and atrophy of the other can cause the spine to become curved. This can be caused by one-sided carrying of heavy objects or unilateral movements. Musicians (for example violinists) or some athletes (for example tennis players) are particularly often affected by muscular imbalances. Muscular imbalances can be counteracted with intensive stretching exercises and targeted strength training.
Incorrect posture - these are the consequences
The consequences of poor posture are manifold and can have a major impact on health. They range from slight muscle tension to pain in the back or neck, affected organ activity and psychological problems.
- Muscle pain
Muscle pain and tension are probably the most common and harmless consequences of poor posture. The muscles affected are usually those that are under a higher load because of the bad posture. The overload can also lead to the muscles not being able to receive sufficient nutrients and oxygen, which can result in delayed recovery. - Neck and back pain
Similarly common to general muscle pain is pain in the neck and back. They often appear after prolonged sitting or standing, but disappear with movement. The more the poor posture progresses, the more likely it is to suffer from chronic postural deformities. These postural defects include scoliosis, a hollow back, a hunchback as well as a flat back.The intervertebral discs also suffer from incorrect posture - under certain circumstances it can promote a herniated disc.
- Organ activity
Anyone who has ever eaten sitting on the floor, bent forward, has probably experienced it: an uneasy stomach feeling or even abdominal pain afterwards. The reason for this is that the digestive organs are compressed in this posture and thus cannot work optimally. A similar thing happens if you have a round back. Not only the stomach and intestines suffer from a bad posture, but also the organs in the chest are easily compressed. Breathing problems or even problems with the cardiovascular system may appear. - Mood and behaviour
That poor posture has physical consequences is to be expected and completely understandable. But who would have thought that an upright posture has a positive effect on our psyche? Studies show that our perception and memory are influenced by our posture. Through good posture, we perceive ourselves and our environment more positively, and we remember more positive things instead of negative ones. Our self-confidence is strengthened. Resistance to stress is also promoted by a straight back. So: keep your head up - in the truest sense of the word! - Attractiveness and effect on others
Not only self-perception is influenced by posture, but also the effect on other people. Non-verbal communication such as facial expressions and gestures play an important role in appearance, and good posture makes you more convincing and trustworthy. This will definitely benefit you at the next job interview or date.
Good posture - how to
The basis for correct posture is high body tension and an upright posture. This is characterised by a hip-width stance, a straight back, relaxed shoulder blades and a neutral, natural head position. The belly button should be drawn toward the spine and the knees slightly bent.
Four exercises for a healthy back and good posture
Many posture exercises are based on yoga poses, as they are particularly gentle on the joints and gently stretch and build the muscles.
Child's Pose
Eliminates pain in the shoulders and upper back.
- Kneel with your shins on your mat.
- Place your arms on the floor beside you with the backs of your hands facing down to create a comfortable stretch in your upper back and shoulders.
- Then extend your arms forward with palms facing the floor and push your buttocks back toward your heels.
- Rest your forehead on the mat and hold the position for up to 30 seconds. You can repeat the exercise two or three times.
Cat-Cow Pose
Good for the spine, neck and shoulders.
- Stand on all fours on your mat, arms extended directly under your shoulders, back straight, knees at right angles on the mat.
- Form an arch in your torso by pressing your abdomen down, extending the curve to the crown of your head and looking up.
- Hold this position briefly and then do the exact opposite by rounding your spine, pulling your belly in and bringing your chin to your chest.
- Repeat the exercise five to ten times and enjoy the relief these movements bring.
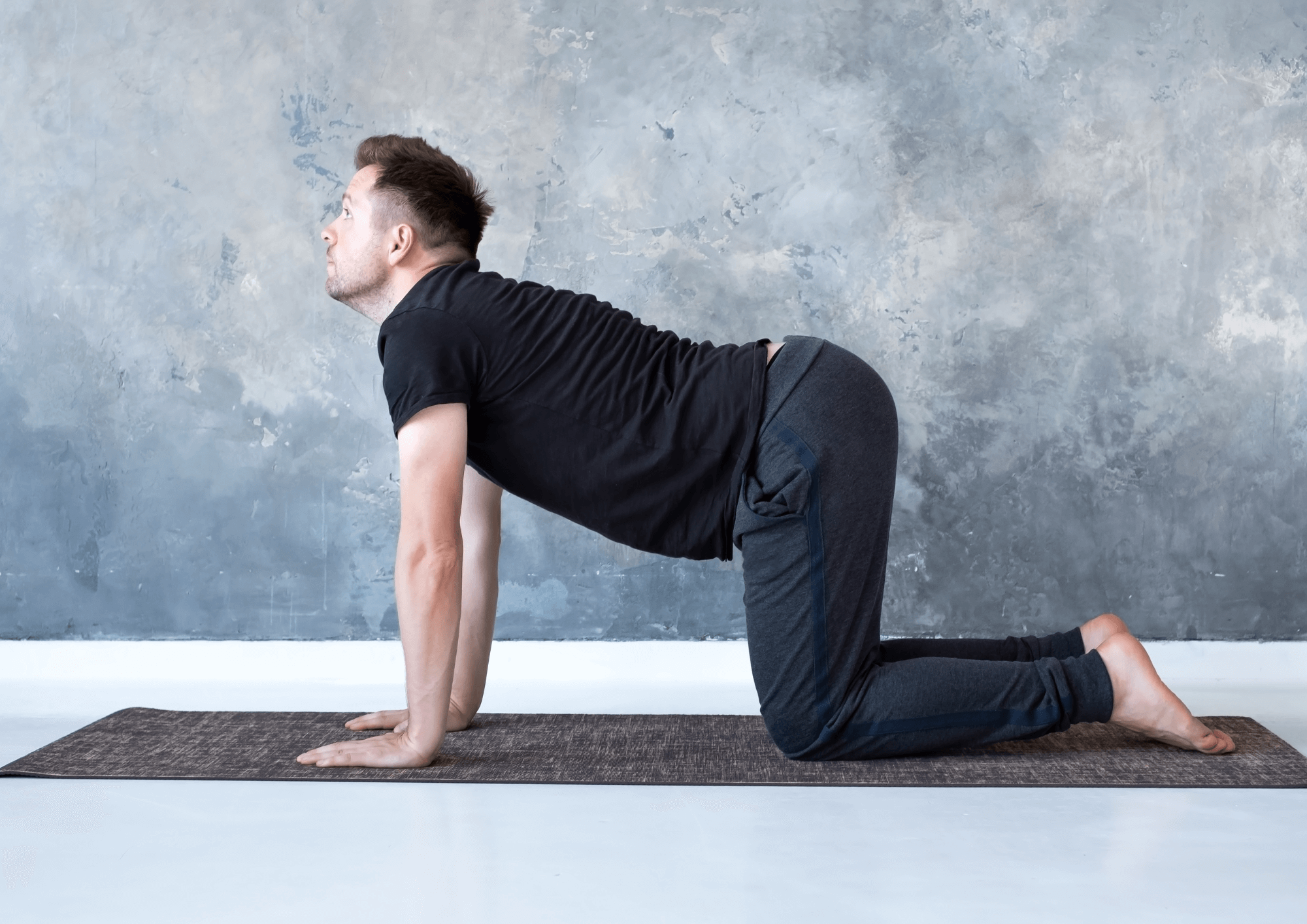
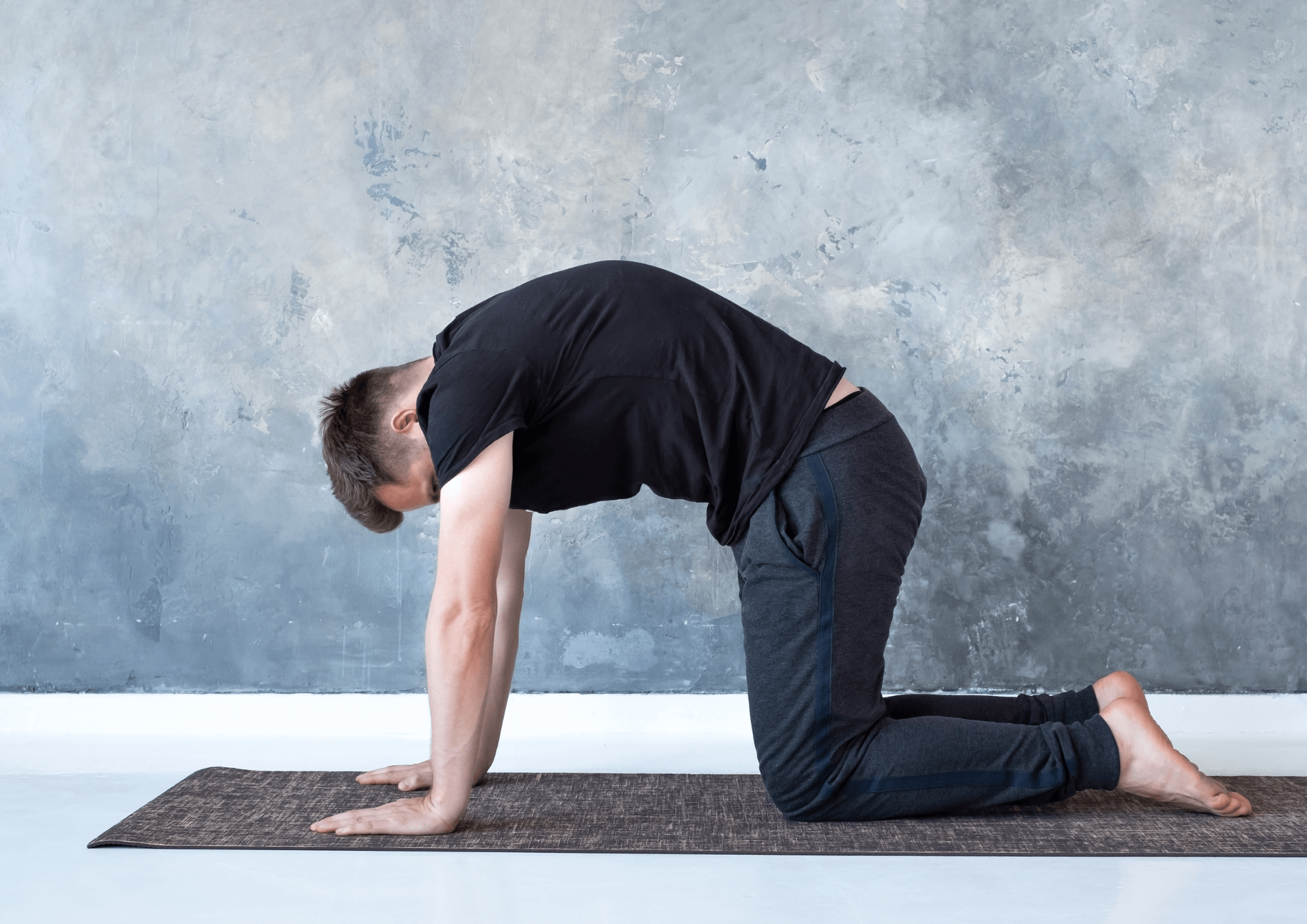


This easy exercise does wonders for your posture.
Neck stretch
For pain and tension in the neck area
- Sit upright on your mat and place one palm on the opposite side of your face.
- Gently tilt your head to the side, and support or increase the stretch with light pressure.
- After a few seconds, turn your head back to the center and repeat the exercise on the other side.
- You can repeat the neck stretch five times on each side.
Chest stretch with open door
Stretches the pectoral muscles and opens the chest muscles.
- Stand in an open door frame and let your palms, forearms and elbows rest on the frame at right angles.
- Take a small step forward through the doorway so that your chest is slightly in front of your arms, and feel the gentle stretch. Be careful not to create too much of a stretch so that you don't overload the muscles.
- Hold this position for about 20 seconds and then repeat two or three times.
Additional tips to prevent bad posture
In addition to the exercises listed above, there are some tips and tricks for everyday life that can help you prevent poor posture.
Ergonomics at work
The fact that we spend too much time sitting is nothing new. It is therefore all the more important that we also pay attention to good posture while sitting and that we set up the office environment ergonomically. The following points are important to make your workday as healthy as possible:
- Office chair: the height of your chair should be adjusted so that your legs form an angle of about 90 degrees, while your feet are flat on the floor. There should be a small space between the seat and the back of your knees. The backrest should support your lower back when sitting upright.
- Office desk: The height of the desk should be adjusted so that your elbows rest loosely on the desk. You should not have to raise your shoulders when doing this.
- Standing up regularly: Get up from your desk several times a day and take a standing or moving break. It's a plus if you have a standing desk at your disposal - the variety is good for your back!
Sports and exercise
It's no news that sports and regular exercise are good for us. For a firm posture, it is especially important to build up muscles in the back and abdomen, as these muscles help you to maintain good body tension.
Correct sleeping position
We sleep an average of 24 years in a lifetime - so it's worth investing in good mattresses and training yourself to sleep in the right position. The following findings have been made by medical experts on different sleeping positions:
- Supine position:
This sleeping position is considered particularly healthy, as it distributes the body weight optimally and supports the spine evenly. A notable plus: the head lies straight - unwanted wrinkles are prevented. The only problem with the supine position: the tongue slips back more easily, which can narrow the airways and increase snoring. - Prone position:
Bad news for all stomach sleepers: this position is not good for the spine, as it works against its natural S-shape. If you can't do without it, you should sleep on as hard a mattress as possible to avoid "bending" your spine even more. - Lateral position:
The fetal position relieves pressure on the vertebral bodies and is therefore good against back pain. But: It can lead to pain in the hips and shoulders. It is interesting to note that lying on the left side is better than on the right. This is because lying on the right side puts more pressure on the lungs and heart, and heartburn is also more common as a result.
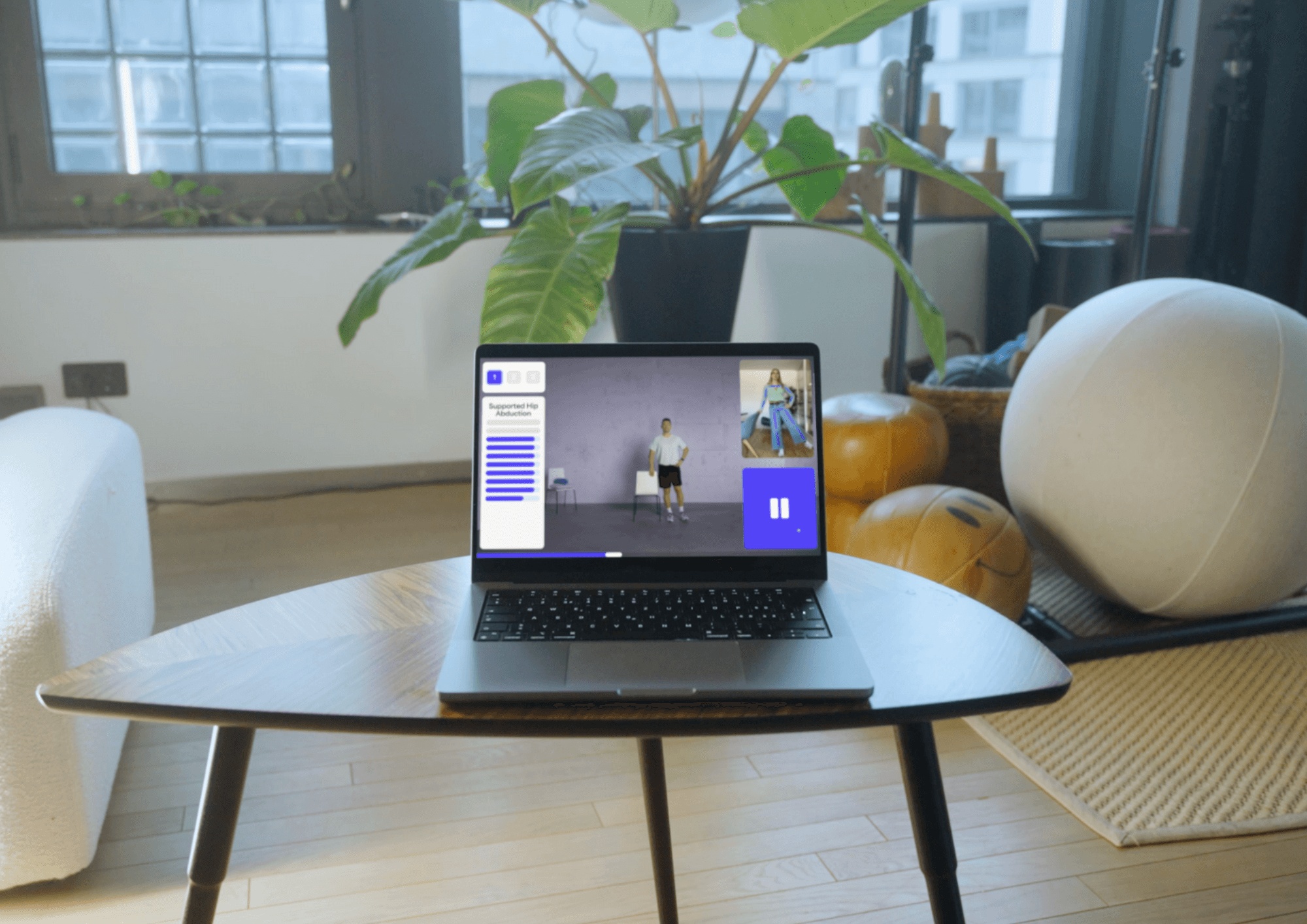
Akina - Better starts today
Do you also suffer from poor posture due to back problems? Start today with targeted, therapeutical back training and say goodbye to pain and limited mobility.
Akina Cloud is an AI-powered medical software that allows you to seamlessly continue your doctor-prescribed physical therapy at home. Our program uses the webcam in popular smart devices like your phone or laptop to analyse and annotate your movements in real time. With a personalised user experience, Akina motivates you to reach your full potential. Through a connected portal, your physical therapist can track your progress and adjust the therapy plan if necessary - for fast and effective treatment.